Beta indicates the stock’s volatility in relation to the market. In general, a beta less than 1 indicates that the investment is less volatile than the market, while a beta more than 1 indicates that the investment is more volatile than the market. For example, if a stock’s beta is 1.25, it’s theoretically 25% more volatile than the market. Conversely, if stock’s beta is 0.6, it is theoretically 40% less volatile than the market.
Higher-beta stocks tend to be more volatile and therefore riskier, but provide the potential for higher returns. Lower-beta stocks pose less risk but generally offer lower returns.
A beta greater than 1 generally means that the asset both is volatile and tends to move up and down with the market. Negative betas are possible for investments that tend to go down when the market goes up, and vice versa. There are few fundamental investments with consistent and significant negative betas, but some derivatives like put options can have large negative betas. Beta can be zero. Some zero-beta assets are risk-free, such as treasury bonds and cash. However, simply because a beta is zero does not mean that it is risk-free.
Beta value summary:
- Beta < 0: Negative Beta – not likely.
- Beta = 0: Cash in the bank.
- Beta Between 0 and 1: Low-volatility
- Beta = 1: Matching the market.
- Beta > 1: More volatility that is greater than the market.
Advantages of using Beta
The beta of a stock gives an idea of the risk involved in buying that stock. If you are a trader looking for stocks that fluctuate a lot, then you can trade in high beta stocks. Knowing that you have high beta stocks in your portfolio also tells you that your portfolio is more prone to risk and fluctuation.
Having beta to determine volatility, you possibly can better choose those securities that match your criteria for risk. Investors who are likely to handle less risk in their investments may want to invest in stocks with low betas. Those investors who are likely to handle more risk may want to invest in stocks with higher betas.
Disadvantages of using Beta
It is important to note that beta is a historically calculated value dependent on how a stock moves compared to a benchmark index. Let’s say a company Y has been a low beta stock historically. When it enters a new business and assumes high debt levels, Y’s historic beta no longer captures the substantial risks the company takes on. At the same time, many IPO stocks that are relatively new to the market have insufficient price history to establish a reliable beta.
How to Find Stocks with High Beta
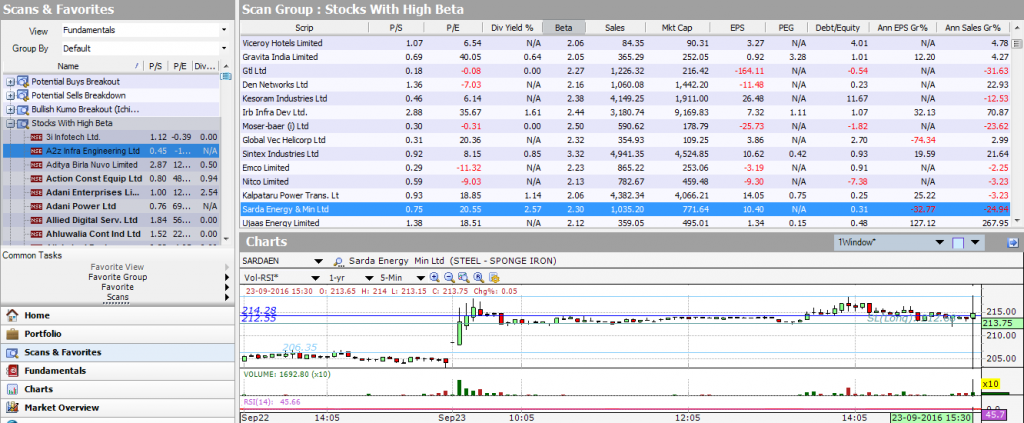
Investar 5.4 has introduced new scans “Stocks with High Beta”. All you have to do is to select the scans from the Predefined Scans list.
You can view the list of high Beta scans conveniently as follows:
- In Manage Scans, select the scan Stock with High Beta
- Change the Favorite View to Fundamentals
- Select View Scans /Favorites with Charts
- On the top will be the list of stocks with a Beta column.
- Click on any stock to see it’s chart at the bottom.
Beta is always measured in respect to some benchmark. Therefore, an asset may have different betas depending on which benchmark is used. Just a number is useless if the benchmark is not known.
For traders looking to buy and sell stocks within short time periods, beta is a fairly good risk metric. However, for investors with long-term horizons, it’s less useful.

Is it (beta) based on EOD value? At what periodicity it changes?
The Beta is calculated using the 1st trading day’s close of every month in a 60-month period.