Option Chain and Option Greeks are two of the most important concepts in options trading. However, they can be quite complex to understand, especially for beginners. In this blog post, we’ll break down the key aspects of Option Chain and the vital role that Option Greeks play in making better trading decisions.
Demystifying Option Chain
Let’s start by understanding Option Chain. Option Chain is an indispensable tool for options traders as they provide a comprehensive list of available options for a specific asset. They include both call and put options with varying strike prices and expiration dates. Think of it as a menu of choices that gives you the flexibility to build trading strategies according to your market outlook and risk tolerance.
Structure of an Option Chain
Strike Prices: The Option Chain lists various strike prices, which represent the prices at which you can buy or sell the underlying asset.
Expiration Dates: Options contracts have expiration dates, which dictate the timeframe within which the contract can be exercised.
Call option: A call option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
Put option: A put option gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
Bid-Ask Prices: These are the current market prices at which buyers are willing to purchase (bid) and sellers are willing to sell (ask) the option.
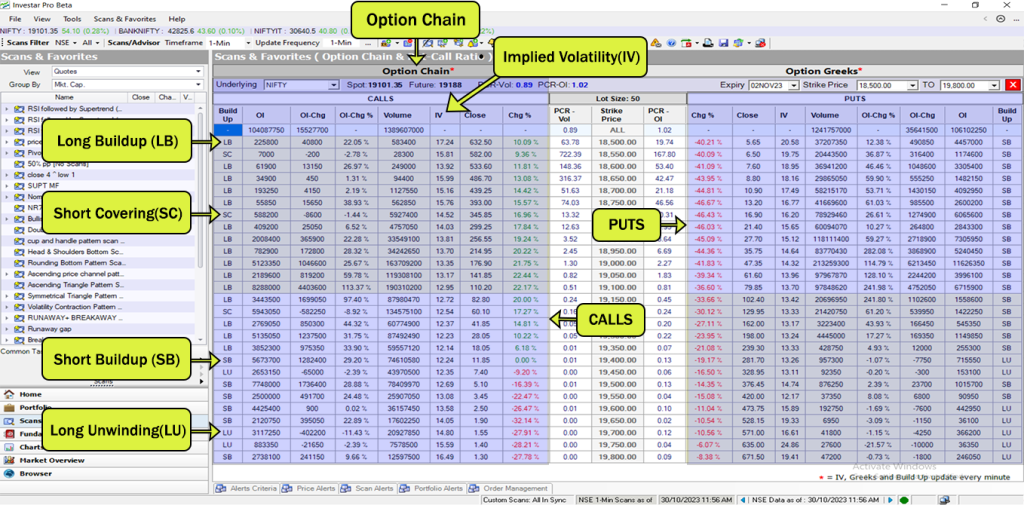
Long Buildup (LB): A long buildup in an option chain occurs when the option price increases, and the open interest also increases. This suggests that traders are becoming more bullish on the underlying asset and are buying call options in anticipation of a price increase.
Short Buildup (SB): A short buildup in an option chain occurs when the option price decreases or remains the same, and open interest increases. This suggests that traders are becoming more bearish on the underlying asset and are buying put options in anticipation of a price decrease.
Long Unwinding (LU): A long unwinding in an option chain occurs when the option price decreases, and open interest decreases. This suggests that traders are becoming less bullish on the underlying asset and are selling call options to lock in profits or reduce their risk.
Short Covering (SC): A short covering in an option chain occurs when the option price increases or remains the same, and open interest decreases. This suggests that traders are becoming less bearish on the underlying asset and are selling put options to lock in profits or reduce their risk.
Implied Volatility (IV): Implied volatility is a measure of the expected volatility of an underlying asset over the life of an option contract. It is calculated using the option’s price, strike price, expiration date, and risk-free interest rate. High IV indicates that traders expect the underlying asset to be volatile, while low IV indicates that traders expect the underlying asset to be stable.
Investar Software Option Chain Data
Investar Software’s Option Chain is a powerful tool that provides traders with a comprehensive overview of options trading data for various indices. It offers real-time insights into long buildup, short buildup, short covering, and long unwinding activity for each strike price, enabling traders to gauge market sentiment and make informed trading decisions. With its user-friendly interface and timely updates, Investar’s Option Chain streamlines the process of selecting the right option strikes for your trading strategy. It is an indispensable resource for both novice and experienced options traders alike, helping them maximize their trading potential.
Unlocking the Power of Option Greeks
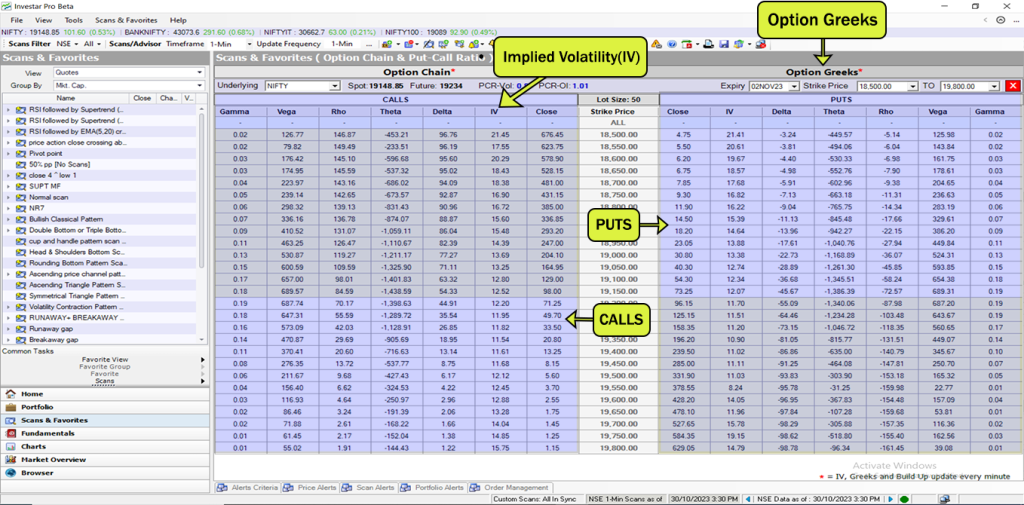
Option Greeks, on the other hand, are a set of risk measures that help traders evaluate the impact of different factors on their options positions. There are five primary Option Greeks: Delta, Gamma, Vega, Theta, and Rho. Let’s delve into each of them briefly:
Delta – The Sensitivity Indicator: Delta measures the change in an option’s price with respect to changes in the underlying asset’s price. It ranges from 0 to 1 for call options and from -1 to 0 for put options. For instance, a Delta of 0.5 means that for every Rs 1 change in the underlying asset’s price, the option’s price will change by Rs 0.50.
Gamma – The Rate of Change: Gamma quantifies the rate of change in Delta concerning variations in the underlying asset’s price. It’s a measure of Delta’s sensitivity to price movements, with higher Gamma indicating a more significant change in Delta with respect to the price movement.
Vega – The Volatility Influencer: Vega assesses the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in implied volatility. It’s crucial for understanding how option prices respond to shifts in market sentiment. High Vega values indicate that option prices are more responsive to volatility changes.
Theta – The Time Decay Factor: Theta measures the time decay of an option. As time passes, an option’s value decreases due to Theta. Traders need to be aware of Theta’s impact, especially when holding options positions.
Rho – Interest Rate Sensitivity: Rho indicates how an option’s price is influenced by changes in interest rates. Although not as commonly discussed as other Greeks, Rho is still critical for certain trading strategies.
Investar Software Option Greeks Data
Leveraging Option Greeks for Better Decisions
Understanding how Option Greeks impact your options is fundamental to constructing effective trading strategies. For instance, if you anticipate a bullish movement in a stock and want to minimize the impact of time decay, you may seek options with higher Delta and lower Theta.
Practical Applications
Option Greeks have numerous practical applications in the real world of trading. They enable traders to assess the risk associated with their positions and to formulate strategies that can mitigate potential losses. For example, if you’re expecting a spike in market volatility, options with higher Vega values might allow you to profit from increased premiums.
Calculating Option Greeks
Traders can calculate Option Greeks using various mathematical models, such as the Black-Scholes model. These models consider factors like time to expiration, implied volatility, and interest rates to determine the values of Delta, Gamma, Vega, Theta, and Rho.
Understanding the Risks and Rewards
It’s crucial to understand that options trading comes with risks. While Option Greeks can help manage these risks, losses are still possible. Therefore, only invest what you can afford to lose, and always make well-informed decisions.
Hedging Strategies
Hedging involves taking offsetting positions to reduce risk. Understanding Option Greeks allows traders to develop effective hedging strategies to protect their investments.
The Role of Volatility
Volatility plays a significant role in options trading. High volatility results in more substantial price swings and greater potential gains or losses. Option Greeks provide insights into how options respond to changes in volatility.
How to use Option Chain and Option Greeks
Option Chain and Option Greeks can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Identifying trading opportunities: Option Chain and Option Greeks can be used to identify oversold and overbought stocks, as well as stocks that are likely to make big moves in the future.
- Managing risk: Option Greeks can be used to hedge your stock portfolio and reduce your risk. For example, if you are long a stock, you could buy a put option on the stock to limit your losses if the stock price falls.
- Creating directional trading strategies: Option Chain and Option Greeks can be used to create directional trading strategies that profit from rising or falling stock prices.
- Trading volatility: Option Chain and Option Greeks can be used to trade volatility. For example, if you believe that volatility is going to increase, you could buy calls on VIX, a volatility index.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the use of Option Chain and Option Greeks can significantly elevate your options trading skills. These tools empower you to navigate the complexities of the market and make well-informed decisions, ultimately improving your chances of success.